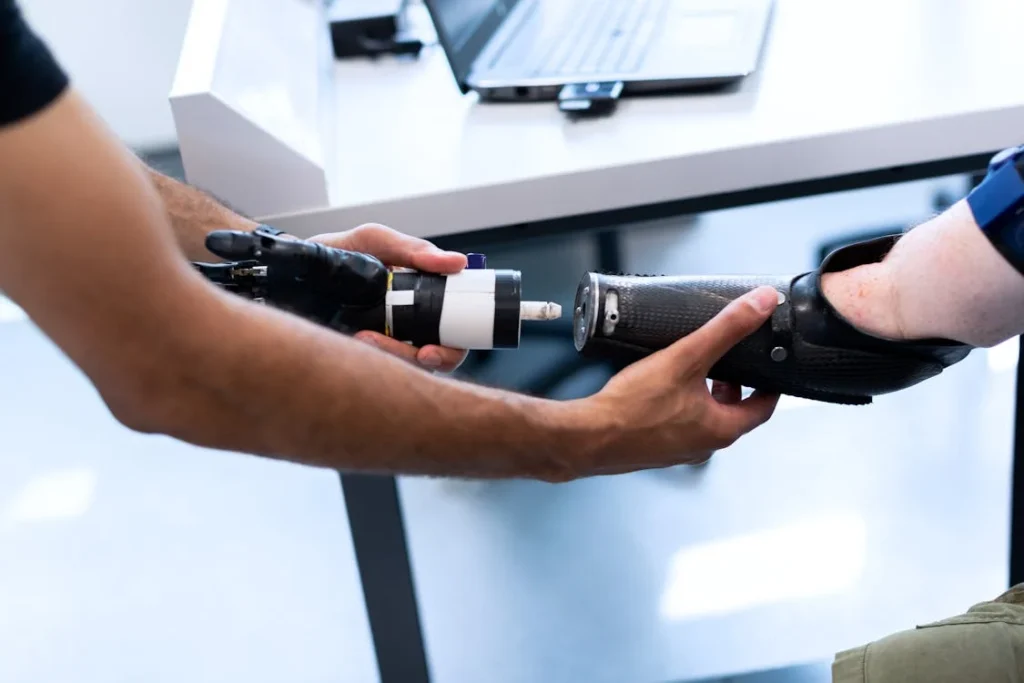
The field of prosthetics has come a long way from its early days of rudimentary wooden limbs. Today, technology is transforming not just the functionality of prosthetic devices but also how they are maintained. Maintenance, once a manual and reactive process, has become smarter, more precise, and proactive, thanks to innovations like sensor technology, connectivity, and data-driven insights.
This shift in approach is changing the lives of prosthetic users, empowering them with tools and solutions that ensure their devices remain functional and reliable for longer. The integration of advanced technologies into prosthetic maintenance is not just about convenience—it’s about enhancing comfort, safety, and independence for users around the world.

The Role of Technology in Modern Prosthetics
Technology has transformed the landscape of prosthetics, making devices more functional, adaptable, and user-centered. Modern prosthetics are no longer static tools—they are dynamic, high-tech systems designed to integrate seamlessly into users’ lives.
At the heart of this evolution is the use of advanced materials, smart sensors, and connectivity, which together redefine how prosthetics are maintained and optimized for daily use.
Enhancing Prosthetic Durability
Prosthetic devices are subjected to significant wear and tear due to daily use, environmental exposure, and varying activity levels.
While traditional maintenance methods relied heavily on user feedback and scheduled check-ups, technology now enables a more proactive approach.
Advanced materials like carbon fiber composites and titanium alloys are being used to build prosthetics that are both lightweight and resilient.
These materials reduce the likelihood of frequent repairs, but technology goes further by providing ways to monitor their condition in real time.
Sensors embedded in prosthetic components can detect stress, pressure, and wear, sending alerts to users and prosthetists before damage becomes critical. This ensures timely interventions and reduces the risk of sudden failures that could disrupt daily life.
Monitoring Performance Through Smart Sensors
One of the most significant advancements in prosthetic maintenance is the integration of smart sensors. These sensors collect data on the prosthetic’s performance, such as gait patterns, pressure distribution, and alignment.
For instance, if a prosthetic limb is slightly misaligned, it can cause discomfort or lead to long-term joint strain. Sensors can identify these issues early by analyzing deviations from optimal performance.
This data is then relayed to the user’s smartphone or directly to their prosthetist, enabling precise adjustments that improve comfort and functionality.
Creating Durable and Adaptable Prosthetics
The materials used in modern prosthetics are far more advanced than those in earlier designs.
Lightweight, durable materials like carbon fiber, titanium, and advanced polymers provide the necessary strength and flexibility to endure rigorous activity while remaining comfortable for users.
These materials are also tailored to specific needs. For example, athletes benefit from prosthetics designed with shock-absorbing capabilities, while water-resistant materials cater to swimmers or users frequently exposed to wet environments.
Beyond durability, these innovations reduce the frequency of wear-related issues, simplifying long-term maintenance.
Advanced materials are often combined with modular designs that allow users to customize or upgrade components as their needs evolve. This adaptability ensures that prosthetics remain effective even as lifestyles, activities, or environments change.
The Rise of Smart Sensors
Sensors are revolutionizing prosthetic technology by providing real-time feedback about device performance and user interaction.
These sensors measure critical data such as pressure, temperature, alignment, and gait dynamics, creating a complete picture of how the prosthetic is functioning.
For example, sensors in a prosthetic foot can monitor weight distribution during walking or running.
If uneven patterns are detected, the device can alert the user or prosthetist to make adjustments, ensuring better alignment and reducing strain on the body. This proactive feedback reduces the risk of long-term discomfort or injury.
Some advanced prosthetics even feature myoelectric sensors, which use electrical signals from the user’s muscles to control movements. These sensors improve precision and responsiveness, making the prosthetic feel like a natural extension of the body.
The Impact of Connectivity on Maintenance
Connectivity has taken prosthetics from standalone devices to integrated systems. Modern prosthetics can connect to smartphones, tablets, and cloud platforms, enabling users to monitor performance, access maintenance insights, and receive alerts about potential issues.
For example, a user might receive a notification if a joint requires lubrication or if a component shows signs of wear. This level of connectivity simplifies maintenance by making it part of the user’s daily routine.
Instead of waiting for noticeable problems to occur, users can address issues as soon as they arise, reducing the risk of downtime or costly repairs.
Prosthetists also benefit from connectivity. By accessing data remotely, they can monitor their patients’ prosthetics, suggest adjustments, and even troubleshoot minor issues without requiring an in-person visit.
This approach improves care accessibility, especially for users in remote areas or those with mobility challenges.
The Role of Precision Engineering
Technology has elevated the precision with which prosthetics are designed and manufactured.
Advanced imaging tools like 3D scanning and CAD (computer-aided design) software enable prosthetists to create custom-fit sockets and components tailored to the unique contours of each user’s body.
This precision minimizes issues related to poor fit, such as skin irritation, pressure points, or reduced mobility. A well-fitted prosthetic not only enhances comfort but also reduces the likelihood of misalignment or wear, contributing to the device’s longevity.
Additionally, 3D printing has emerged as a game-changer in prosthetic manufacturing. This technology allows for the rapid production of highly customized components, often at a lower cost than traditional methods.
Users benefit from faster turnaround times and more affordable access to tailored solutions.
Technology as a Partner in User Empowerment
The integration of technology into modern prosthetics goes beyond functionality—it actively empowers users. Advanced features like customizable settings, intuitive controls, and interactive interfaces make it easier for users to take charge of their prosthetic experience.
For instance, users can fine-tune the sensitivity of their prosthetic’s sensors or select activity-specific modes for tasks like running, climbing, or lifting. This level of personalization ensures the device adapts to their unique lifestyle rather than the user adapting to the device.
Connectivity and Data Analytics in Prosthetic Care
Connectivity and data analytics have redefined how prosthetics are maintained and optimized, creating a bridge between user experiences and technological advancements.
Through seamless integration with digital platforms, these innovations enable prosthetic devices to provide real-time insights, improve performance, and empower both users and professionals to make informed decisions.
The Power of Connectivity
Modern prosthetics are no longer standalone devices; they are part of an interconnected ecosystem that enhances their functionality and maintenance.
The integration of wireless technology, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, allows prosthetics to connect seamlessly with smartphones, tablets, and even cloud-based systems.
This connectivity provides users with instant access to performance data and maintenance insights. For example, a user can receive real-time notifications about battery levels, alignment issues, or component wear directly on their smartphone.
This immediate feedback eliminates guesswork and ensures that users can address potential problems before they escalate.
For prosthetists, connectivity offers a new level of engagement with their patients. They can monitor the condition of a prosthetic remotely, provide adjustments, and even troubleshoot minor issues without requiring an in-person visit.
This capability reduces the need for frequent appointments and provides greater convenience for users.
Harnessing Data Analytics
Data analytics is revolutionizing how prosthetic maintenance is approached. The wealth of information collected by smart prosthetics—such as usage patterns, stress levels, and environmental exposure—can be analyzed to gain valuable insights.
These insights enable prosthetists to develop tailored maintenance schedules based on individual needs rather than relying on generalized timelines.
For example, a prosthetic used by an athlete may require different maintenance compared to one used by someone with a sedentary lifestyle.
Data analytics also allows for the identification of trends and potential risks. If a particular component consistently shows signs of wear under specific conditions, manufacturers can address this by improving the design or material.
Creating a Seamless Ecosystem
Modern prosthetics are no longer isolated tools; they are part of a larger connected ecosystem that integrates with smartphones, cloud services, and even other medical devices.
This connectivity allows users to access vital information about their prosthetic’s performance anytime and anywhere.
For example, a prosthetic with Bluetooth capabilities can connect to an app, enabling users to monitor battery levels, analyze gait patterns, and adjust settings for specific activities like walking, running, or cycling.
These interactions are designed to be intuitive, making it easier for users to personalize their device to match their lifestyle.
For professionals, connectivity offers a wealth of opportunities to support users remotely. Prosthetists can review data transmitted from the prosthetic to assess wear patterns, alignment issues, or sensor performance.
This ongoing monitoring allows for proactive care, minimizing the need for in-person visits and addressing issues before they affect the user’s mobility.
Real-Time Insights for Users
Connectivity transforms prosthetic maintenance from a reactive process into a proactive one by delivering real-time insights directly to users. These insights allow users to take immediate action, preventing small issues from escalating into significant problems.
For instance, if a joint in the prosthetic starts experiencing abnormal stress, the connected app might send a notification suggesting lubrication or adjustment.
Similarly, if a battery is nearing depletion, the app can alert the user to charge the device before it impacts functionality. These timely reminders reduce downtime and ensure that users can rely on their prosthetics in any situation.
The ability to access real-time data also enhances the user’s confidence in their device. Knowing that potential issues are detected early and can be resolved quickly creates a sense of security and encourages users to engage more actively in their daily activities.
Harnessing Big Data for Improved Care
Data analytics is a powerful tool in prosthetic care, providing valuable insights into usage patterns, environmental exposure, and performance trends.
When prosthetics are equipped with sensors and connected to cloud platforms, they generate large volumes of data that can be analyzed to improve maintenance strategies.
For users, this data provides a deeper understanding of how their prosthetic interacts with their body and environment. They can review reports on metrics such as stride length, pressure distribution, or activity duration, identifying areas for improvement or adjustment.
This personalized feedback helps users refine their movements, reduce discomfort, and maximize the efficiency of their prosthetic.
For manufacturers and prosthetists, aggregated data from multiple users highlights broader trends that can guide product development. If certain components consistently show wear under specific conditions, manufacturers can refine designs to enhance durability.
Prosthetists can also use this data to tailor maintenance schedules based on the user’s unique habits and needs.
Predictive Maintenance Powered by Analytics
One of the most transformative aspects of data analytics in prosthetic care is its role in predictive maintenance. By analyzing historical and real-time data, predictive analytics identifies patterns that signal potential issues before they occur.
For example, if data shows a gradual increase in joint resistance or a decline in battery efficiency, the system can recommend maintenance or part replacement before the issue impacts performance.
This approach not only minimizes disruptions but also extends the prosthetic’s lifespan by preventing unnecessary strain on its components.
Predictive maintenance also reduces costs for users. By addressing issues proactively, users can avoid emergency repairs or unexpected downtime, making their overall experience more seamless and stress-free.
Enhancing Accessibility and Equity
Connectivity and data analytics also play a crucial role in making prosthetic care more accessible, particularly for users in remote or underserved areas.
Remote monitoring enables users to receive professional support without the need for frequent in-person visits, overcoming barriers such as travel limitations or lack of nearby prosthetic clinics.
Additionally, data-driven insights empower users to take charge of their own care, reducing dependence on external resources.
By combining these tools with telehealth consultations, users can receive comprehensive support regardless of their location, ensuring that advanced prosthetic care is within reach for everyone.
The Future of Connected Prosthetics
The potential of connectivity and data analytics in prosthetic care is only beginning to be realized. Emerging technologies, such as edge computing and 5G networks, promise to enhance the speed and accuracy of data processing, enabling even more sophisticated features.
Future prosthetics may integrate with other health monitoring devices, such as fitness trackers or medical sensors, creating a holistic view of the user’s health and mobility.
This interconnected approach would allow for even greater personalization, as prosthetics adapt dynamically to the user’s physical and environmental conditions.
Advancements in Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics is revolutionizing prosthetic care by enabling issues to be identified and addressed without the need for in-person appointments. This innovation has transformed prosthetic maintenance from a reactive process into a proactive, user-centered approach.
With the integration of smart sensors, connectivity, and advanced analytics, remote diagnostics not only improves the user experience but also enhances the reliability and longevity of prosthetic devices.
Identifying Issues Without Disruption
One of the most transformative aspects of modern prosthetic care is the advent of remote diagnostics. This technology enables users to identify and address potential issues without interrupting their daily lives.
Remote diagnostics work by combining smart sensors, connectivity, and data analysis. When a prosthetic detects a problem—such as increased friction in a joint or a drop in battery efficiency—it can automatically send this information to the user’s prosthetist.
The prosthetist can then assess the issue remotely and recommend appropriate solutions.
This approach reduces the need for in-person appointments and provides peace of mind to users, knowing that their prosthetic is being monitored for optimal performance at all times.
For those living in remote areas or with limited access to specialized care, remote diagnostics is a game-changer.
Preventing Major Failures
By identifying minor issues early, remote diagnostics prevent them from escalating into major failures. For instance, if a mechanical component shows signs of stress, the prosthetist can intervene with a repair or replacement before it affects the user’s mobility.
This proactive approach not only saves time and money but also ensures that users can rely on their prosthetic without worry.
Bridging the Gap Between Users and Professionals
One of the most significant impacts of remote diagnostics is its ability to bridge geographical and logistical gaps. For users in remote locations or those with limited mobility, accessing prosthetic care can be challenging.
Remote diagnostics addresses this by allowing prosthetists to monitor and analyze device performance from a distance.
For example, sensors embedded in the prosthetic continuously collect data on alignment, pressure, and stress. This data is transmitted to a secure cloud platform, where prosthetists can access it in real time.
If the system detects any irregularities—such as increased resistance in a joint or uneven weight distribution—it alerts the prosthetist, who can then recommend adjustments or repairs.
This capability ensures that users receive timely care, reducing the need for frequent clinic visits while maintaining optimal device performance.
It also minimizes disruptions to the user’s daily routine, as minor issues can often be resolved remotely through guidance or software updates.
Early Detection of Potential Problems
Remote diagnostics excels in identifying potential problems before they escalate into significant issues. By continuously monitoring the prosthetic’s performance, the system can detect subtle changes that may not be immediately noticeable to the user.
For instance, a gradual misalignment in a knee joint might cause discomfort over time and eventually lead to long-term complications.
With remote diagnostics, this misalignment can be identified early, allowing the prosthetist to provide precise instructions for correction or schedule a targeted adjustment.
Early detection not only prevents damage to the prosthetic but also protects the user from discomfort, pain, or mobility challenges. This proactive approach saves time, reduces costs, and fosters confidence in the device’s reliability.
Enhancing User Confidence
Remote diagnostics empowers users by giving them access to detailed information about their prosthetic. Many systems include user-friendly apps or dashboards that display real-time data on the device’s condition, performance, and maintenance needs.
For example, a user can monitor battery health, view activity summaries, or receive alerts about potential issues. This transparency builds trust and confidence, as users can see firsthand how their prosthetic is performing.
They also gain a deeper understanding of their device, making them active participants in its care and maintenance.
Additionally, knowing that their prosthetic is being monitored remotely provides users with peace of mind. Even in the absence of visible problems, they can feel assured that any potential issues will be detected and addressed promptly.
Facilitating Customization and Fine-Tuning
Every prosthetic user has unique needs and preferences, and remote diagnostics facilitates the customization and fine-tuning of devices to meet these requirements.
By analyzing usage patterns and environmental data, prosthetists can make precise adjustments that enhance comfort and functionality.
For example, if a user frequently engages in activities that place additional strain on specific components, remote diagnostics can identify these stress points.
Prosthetists can then recommend modifications, such as reinforcing vulnerable areas or optimizing alignment for better performance during high-impact activities.
This level of customization ensures that the prosthetic evolves with the user’s lifestyle, rather than requiring the user to adapt to the device. It also extends the device’s lifespan by reducing unnecessary wear and tear.
Reducing Downtime Through Remote Updates
Another critical advantage of remote diagnostics is its ability to reduce downtime by enabling remote updates and minor repairs.
In many cases, issues with electronic prosthetics can be resolved through software updates or recalibration, eliminating the need for in-person servicing.
For example, if a sensor calibration issue affects the prosthetic’s responsiveness, the prosthetist can deploy a remote software update to address the problem. This not only saves time but also ensures that users can continue relying on their device without interruption.
At Robobionics, we integrate remote diagnostics into our prosthetics to provide seamless updates and personalized support, ensuring users experience minimal disruptions to their mobility.
The Future of Remote Diagnostics
As technology continues to advance, the potential for remote diagnostics in prosthetic care will expand even further.
Future developments may include AI-driven diagnostic tools capable of identifying complex issues with greater accuracy, as well as virtual reality (VR) interfaces for guided troubleshooting and adjustments.
Remote diagnostics could also integrate with other health monitoring systems, providing a holistic view of the user’s well-being.
For example, data from the prosthetic could be combined with heart rate, activity level, and posture information to create comprehensive health profiles that inform both prosthetic care and overall health management.

Artificial Intelligence in Predictive Maintenance
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in prosthetic care, particularly in predictive maintenance. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning models, AI enables prosthetics to anticipate potential issues before they occur.
This shift from reactive to predictive care not only enhances the longevity and reliability of prosthetic devices but also empowers users with greater confidence in their mobility.
Anticipating Issues Before They Happen
Artificial intelligence (AI) is taking prosthetic maintenance to a new level by enabling predictive maintenance. Unlike reactive or even proactive approaches, predictive maintenance uses AI algorithms to anticipate potential problems before they occur.
AI analyzes data collected from sensors, such as stress levels, temperature changes, and usage patterns, to predict when a component is likely to fail.
This insight allows users and prosthetists to schedule maintenance or part replacements at the ideal time, avoiding unexpected disruptions.
For example, if an AI system detects a gradual increase in joint resistance, it might suggest lubricating the joint or replacing a worn part before it impacts performance. This precision ensures that maintenance efforts are efficient and effective, extending the lifespan of the prosthetic.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The beauty of AI lies in its ability to learn and adapt over time. As more data is collected, AI systems become better at identifying patterns and predicting outcomes.
This continuous improvement benefits users by providing increasingly accurate and personalized maintenance recommendations.
The Foundation of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance relies on data—large volumes of it. Modern prosthetics are equipped with sensors that continuously monitor key metrics, such as pressure, alignment, and joint resistance.
These sensors generate a wealth of information that AI systems analyze to detect patterns, identify anomalies, and forecast potential failures.
For instance, an AI algorithm might notice a gradual increase in resistance within a joint mechanism. While this change may not immediately impact functionality, the system can predict when the resistance will reach a level that could cause discomfort or mechanical failure.
This foresight allows users and prosthetists to take preemptive action, such as lubricating the joint or replacing a component, well before the issue disrupts daily activities.
Real-Time Analysis and Insights
One of AI’s most significant contributions to predictive maintenance is its ability to provide real-time analysis of a prosthetic’s condition. Unlike traditional diagnostics, which rely on periodic check-ups, AI systems offer continuous monitoring and instant feedback.
For example, if a user’s gait pattern shifts slightly due to uneven wear in a foot prosthetic, the AI system can immediately detect the deviation.
By analyzing historical data and comparing it to real-time inputs, the system can determine whether the change indicates normal usage or an emerging problem. This level of responsiveness ensures that users receive timely alerts and actionable recommendations.
Enhancing Accuracy Through Machine Learning
Machine learning, a subset of AI, plays a critical role in improving the accuracy of predictive maintenance. By analyzing historical data from multiple users, machine learning algorithms continuously refine their understanding of how prosthetics perform under different conditions.
For example, the system might learn that certain materials wear down more quickly in humid environments or that specific activities place higher stress on certain components.
These insights enable the AI to provide more tailored recommendations, such as adjusting maintenance schedules based on the user’s lifestyle or suggesting material upgrades for specific conditions.
Machine learning also helps identify complex relationships between variables that might not be immediately apparent. This deeper understanding allows for more sophisticated predictions, ensuring that even subtle issues are addressed before they escalate.
Reducing Unplanned Downtime
Unplanned downtime—when a prosthetic fails unexpectedly—can significantly impact a user’s mobility and daily life. AI-driven predictive maintenance virtually eliminates this risk by providing early warnings and precise timelines for necessary interventions.
For example, if an AI system predicts that a component will likely fail within the next month, users and prosthetists can plan a replacement at a convenient time, avoiding disruptions.
This proactive approach ensures that prosthetics remain reliable and functional, even under demanding conditions.
Reducing downtime not only enhances the user experience but also extends the lifespan of the prosthetic. By addressing issues early, users can avoid secondary damage caused by prolonged strain on failing components.
Personalization Through AI
Every prosthetic user has unique needs, and AI excels at personalizing maintenance strategies to match these requirements.
By analyzing data specific to each individual, AI systems can create customized care plans that reflect the user’s activity levels, environmental exposure, and preferences.
For example, an athlete may receive more frequent alerts for joint lubrication or alignment checks due to the high-impact nature of their activities.
Conversely, a user with a more sedentary lifestyle might benefit from extended maintenance intervals tailored to their usage patterns.
This level of personalization ensures that maintenance efforts are both efficient and effective, allowing users to focus on their goals without worrying about their prosthetic’s performance.
Supporting Continuous Improvement
AI in predictive maintenance not only benefits users but also drives continuous improvement in prosthetic design and manufacturing.
By analyzing aggregated data from a wide range of users, manufacturers gain valuable insights into how prosthetics perform in real-world scenarios.
For instance, if AI data reveals that a specific material tends to degrade under certain conditions, manufacturers can explore alternatives to enhance durability.
Similarly, insights into common failure points can guide design refinements, resulting in more resilient and user-friendly devices.
The Future of AI-Driven Maintenance
The potential of AI in predictive maintenance is vast, and the future holds exciting possibilities.
As AI systems become more sophisticated, they may integrate with other technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) for guided repairs or virtual assistants that provide step-by-step maintenance instructions.
AI-driven prosthetics could also incorporate environmental sensors that adjust device settings in real time, optimizing performance based on weather, terrain, or activity.
These advancements promise to make prosthetics even more adaptable and intuitive, aligning seamlessly with the user’s lifestyle.

Empowering Users Through Technology
Technology is not just reshaping how prosthetics are designed and maintained; it is transforming how users interact with and feel about their devices.
By integrating advanced features, intuitive tools, and personalized support, modern prosthetics empower users to take control of their mobility and independence. This shift from reliance to self-sufficiency fosters confidence, adaptability, and an enhanced quality of life.
Simplifying Maintenance for Everyday Use
Technology is not only revolutionizing how prosthetic maintenance is performed but also making it more accessible and manageable for users.
Maintenance, once seen as a specialized task requiring professional intervention, is now becoming an integral part of daily routines through user-friendly technology.
Apps and companion software connected to prosthetics allow users to monitor their device’s performance with ease. These platforms provide real-time updates, such as battery status, alignment checks, and component wear, in a clear and straightforward manner.
For users, this means less reliance on guesswork and more confidence in their ability to keep their prosthetic functioning at its best.
Gamification features, such as progress tracking and achievement badges, make the process of maintaining a prosthetic more engaging, particularly for younger users.
Building Confidence Through Knowledge
One of the most significant advantages of technology in prosthetic maintenance is the empowerment it provides to users.
Through educational resources embedded in apps or available online, users can learn about their prosthetics, from how they function to best practices for care.
This knowledge fosters a sense of ownership, enabling users to take an active role in maintaining their device. It also reduces anxiety about unexpected issues, as users feel equipped to recognize and address minor problems on their own.
Building Confidence Through Knowledge
One of the most profound ways technology empowers users is by providing them with actionable knowledge about their prosthetics.
Real-time monitoring, made possible by embedded sensors and connected apps, allows users to gain a deeper understanding of their device’s condition and performance.
For example, an app that tracks metrics like stride length, joint resistance, or pressure distribution equips users with valuable insights into how their prosthetic aligns with their daily activities.
With this information, users can identify areas for improvement, such as adjusting their gait or optimizing the fit of their socket, leading to better comfort and efficiency.
Access to this level of detail transforms the relationship between users and their prosthetics.
Instead of feeling dependent on external support for every concern, users gain the confidence to address minor issues themselves or communicate effectively with their prosthetists when professional intervention is needed.
Encouraging Personalized Interaction
Technology has introduced unprecedented levels of customization to prosthetics, allowing users to tailor their devices to their unique needs and preferences.
Smart interfaces, such as mobile apps or wearable devices, make it easy for users to adjust settings, switch modes, or even select activity-specific configurations.
For example, a user transitioning from walking to cycling can use their app to activate a mode optimized for that activity. This seamless adaptability ensures that the prosthetic feels like an extension of the user’s body rather than a separate tool.
Customization also extends to aesthetics, with options for personalized designs, colors, and materials that reflect the user’s personality. This level of control helps users build a positive relationship with their prosthetic, viewing it as a source of empowerment rather than a limitation.
Reducing Dependence on External Support
In the past, prosthetic maintenance and adjustments often required frequent visits to clinics or prosthetists. While professional care remains essential, technology has significantly reduced users’ dependence on external support for routine tasks.
For example, remote diagnostics and app-based troubleshooting allow users to address minor issues without leaving their homes.
An app might guide a user through recalibrating a joint, cleaning a sensor, or checking for proper alignment. These capabilities not only save time but also reduce the psychological burden of feeling reliant on others for every aspect of prosthetic care.
By enabling users to handle routine maintenance independently, technology fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. This empowerment is particularly impactful for younger users, who benefit from learning how to care for their prosthetics from an early age.
Integrating Prosthetics Into Daily Life
Technology has made it easier than ever to integrate prosthetics into daily routines. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches, can sync with prosthetics to provide discreet reminders or updates, such as when it’s time to charge the device, perform cleaning, or schedule maintenance.
For users with demanding schedules, this integration ensures that prosthetic care becomes a natural part of their day rather than an additional task to manage. It also helps users stay proactive, preventing small oversights from developing into larger issues.
Advanced technology also enhances user experiences in specific environments or activities. For instance, waterproof components allow users to swim or engage in water sports, while shock-absorbing features enable athletes to train confidently.
These advancements reinforce the idea that prosthetics are tools of freedom, enabling users to pursue their goals without restriction.
Empowering Through Accessibility
Accessibility is a cornerstone of user empowerment, and technology plays a critical role in breaking down barriers to prosthetic care.
Remote monitoring and telehealth consultations ensure that users in remote areas or with limited mobility can access expert support without unnecessary travel.
Additionally, digital platforms provide users with educational resources, such as video tutorials, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides.
These tools help users develop a comprehensive understanding of their prosthetic and its care, enabling them to make informed decisions and feel more in control.
For children and young adults, gamified features and interactive learning modules make the process of adapting to a prosthetic engaging and enjoyable.
By turning maintenance and skill-building into a game, these technologies instill confidence and encourage consistent use of the device.
Fostering a Community of Empowered Users
Technology also facilitates connection among prosthetic users, creating a sense of community and shared learning. Online forums, social media groups, and app-based platforms allow users to exchange tips, share experiences, and celebrate milestones together.
These connections provide emotional support and practical advice, reinforcing the idea that users are not alone in their journey. For many, seeing how others have successfully adapted to their prosthetics serves as a source of inspiration and motivation.

Integrating Maintenance Into Daily Routines
Prosthetic maintenance is most effective when it becomes a natural part of daily life. Integrating care into your routine not only ensures your prosthetic remains functional and comfortable but also prevents the build-up of minor issues that can escalate into significant problems.
With advancements in technology and user-centered tools, maintaining a prosthetic has become more intuitive and less time-consuming, making it easier for users to stay proactive.
The Role of Wearable Technology
Wearable technology is making it easier than ever to integrate prosthetic maintenance into daily life. Smartwatches, for instance, can sync with prosthetic devices to provide subtle reminders about care routines, such as cleaning, lubrication, or charging.
These gentle prompts ensure that maintenance tasks are completed regularly without overwhelming the user.
Wearables also make real-time alerts more accessible. For example, if a sensor detects unusual pressure or a drop in performance, a notification can appear on the user’s wrist, prompting immediate action.
This integration of maintenance into everyday life creates a seamless experience that enhances convenience and peace of mind.
Creating Habits That Last
Technology supports the development of long-term habits by automating reminders and providing feedback on maintenance efforts.
For example, a smartphone app might track cleaning frequency or highlight improvements in performance after adjustments. This feedback reinforces positive behavior and helps users stay consistent with care routines.
For children and young adults, incorporating maintenance into daily activities through engaging and interactive technology fosters lifelong habits. These early lessons in responsibility and care ensure they grow into confident, independent users of their prosthetics.
Building Habits for Long-Term Care
Consistency is the foundation of effective maintenance. By making prosthetic care a habitual part of your daily routine, you reduce the chances of neglecting important tasks like cleaning, inspecting, or charging the device.
Over time, these practices become second nature, seamlessly blending into your everyday activities.
Start by identifying moments in your routine where prosthetic care fits naturally. For example, incorporating a quick inspection during your morning or evening routine ensures that potential issues are addressed before they affect your mobility.
Cleaning the prosthetic at the end of the day, after it has been exposed to dirt or moisture, helps maintain hygiene and prevents debris from causing wear and tear.
For users with busy schedules, setting reminders through wearable devices or smartphone apps can help reinforce these habits.
Notifications to clean the socket, adjust the alignment, or check battery levels serve as gentle prompts that keep maintenance on track without feeling intrusive.
Leveraging Technology for Simplified Maintenance
Modern prosthetics come equipped with advanced features that simplify maintenance, making it easier to integrate into daily routines.
Sensors and connectivity tools provide real-time data on the prosthetic’s condition, enabling users to monitor performance effortlessly. For instance, an app might alert you if a joint requires lubrication or if the prosthetic is showing signs of wear.
These technologies also allow users to schedule maintenance tasks based on actual usage rather than arbitrary timelines.
For example, a prosthetic that tracks your activity levels can suggest cleaning or servicing intervals that align with how much the device is being used. This personalization ensures that care routines are efficient and relevant, saving both time and effort.
At Robobionics, we design our prosthetics with intuitive interfaces that empower users to take control of their device’s maintenance. By combining technology with ease of use, we make it simple to integrate care into any lifestyle.
Educating Users on Best Practices
Integrating maintenance into daily life begins with understanding the specific needs of your prosthetic. Users who are well-informed about their device are better equipped to recognize potential issues and address them promptly.
Prosthetists play a key role in educating users on maintenance best practices. During fitting sessions or follow-up appointments, they can demonstrate how to clean the device, inspect for wear, and perform minor adjustments.
Digital tools, such as video tutorials or in-app guides, complement this education by providing step-by-step instructions that users can refer to as needed.
By building a foundation of knowledge, users gain the confidence to incorporate maintenance into their routines without feeling overwhelmed. This empowerment fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, ensuring long-term adherence to care practices.
Creating a Balance Between Maintenance and Convenience
While regular maintenance is essential, it’s important that these routines do not feel burdensome. Striking a balance between thorough care and convenience ensures that maintenance becomes a sustainable habit rather than a source of stress.
For instance, breaking down maintenance tasks into manageable steps makes them easier to fit into a busy day.
A quick wipe-down after outdoor activities, combined with a more thorough cleaning at the end of the week, spreads out the workload while keeping the prosthetic in good condition.
Technology further enhances convenience by automating certain aspects of maintenance. Smart prosthetics equipped with self-diagnostic features can identify and report issues without requiring constant user oversight.
Similarly, modular designs make it easy to replace or upgrade specific components without disrupting the overall functionality of the device.
Instilling Responsibility in Younger Users
For pediatric prosthetic users, integrating maintenance into daily routines serves as an opportunity to instill responsibility and independence.
Parents can involve their children in simple tasks, such as organizing care supplies or wiping down the device, gradually increasing their involvement as they grow older.
Gamified features, such as earning rewards for consistent cleaning or completing maintenance milestones, make the process engaging and enjoyable for young users.
These positive associations encourage long-term adherence to care routines and build confidence in managing their prosthetic independently.
Supporting Active Lifestyles
For users with active lifestyles, integrating maintenance into daily routines ensures their prosthetics can keep up with demanding activities.
Whether it’s an athlete preparing for training or an adventurer exploring new environments, regular care prevents disruptions caused by unexpected issues.
For example, an athlete might incorporate a quick alignment check into their warm-up routine to ensure optimal performance.
Similarly, someone engaging in outdoor activities can include a post-activity cleaning session to remove dirt, sand, or moisture. These small but strategic additions to their routine maintain the prosthetic’s reliability and durability.
Fostering Long-Term Care Habits
Daily maintenance routines are not just about preserving the prosthetic—they’re about fostering habits that support long-term well-being. A well-maintained prosthetic reduces the risk of discomfort, improves mobility, and enhances the overall user experience.
The Future of Prosthetic Maintenance
Innovations on the Horizon
As technology continues to advance, the future of prosthetic maintenance holds exciting possibilities. One area of development is self-healing materials—innovative substances that can repair minor damage on their own.
These materials would reduce the need for frequent repairs and enhance the longevity of prosthetics.
Another promising innovation is the use of augmented reality (AR) in maintenance. AR could guide users through complex care tasks with visual overlays, showing them exactly where to clean, adjust, or inspect.
This hands-on guidance would make even advanced maintenance accessible to all users.
Bridging the Gap Between Users and Professionals
While technology empowers users to manage maintenance independently, the connection between users and prosthetists remains vital.
The future will likely see greater collaboration through telehealth solutions, allowing prosthetists to provide real-time support and adjustments remotely.
AI-driven diagnostic tools, combined with professional expertise, will create a hybrid model of care that blends convenience with precision. This approach ensures users receive the support they need while maximizing the capabilities of modern technology.
Conclusion
Technology is reshaping prosthetic maintenance in profound ways, making it smarter, more accessible, and more user-focused. From real-time monitoring with smart sensors to predictive maintenance powered by AI, these advancements are helping users extend the life of their prosthetics while enhancing their day-to-day experience.
As the industry continues to evolve, innovations like wearable technology, remote diagnostics, and AR-guided maintenance promise to further empower users and simplify care routines. At Robobionics, we are dedicated to integrating these cutting-edge solutions into our prosthetics, ensuring that every user can enjoy greater independence, confidence, and reliability.
The future of prosthetic maintenance is not just about keeping devices functional—it’s about transforming the relationship between users and their prosthetics. Contact us today to learn how our technology-driven solutions can enhance your prosthetic experience and help you achieve new levels of mobility and comfort.



